Types of Bread Packaging
- Release Lime: Aug 28 2019
- Source: Sherry
We can see different types of bread packaging on market. But do you know what they are?
First of all, let's first understand the role of bread packaging, in order to ensure that the bread quality meets the hygiene requirements, the bread after cooling or slicing should be packaged immediately.
1. Keep the bread clean and avoid contamination during storage and transportation.
2. Prevent the bread from hardening and extend the shelf life. From the factory to the consumer, the bread needs to be stored and transported for a period of time. As the starch ages and the water evaporates, the bread will harden. After the bread is packaged, it can avoid a lot of moisture loss and keep the bread fresh.
3. Increase the aesthetics of the product. Beautiful packaging can attract consumers' attention, highlight product features, and expand consumption.
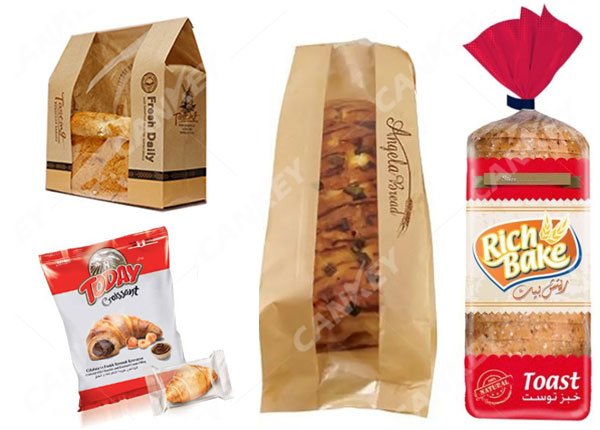

Types of bread packaging:
There are many types of bread packaging, which are divided into folding packaging, shrink packaging, and bag packaging according to the packaging form.
According to the packaging method, it can be divided into manual packaging, semi-mechanized packaging and automated packaging. Manual packaging is less restricted by factors such as funds, venues, and product quantities. The application is more flexible, but the disadvantage is that it may not meet the hygiene requirements. Both semi-mechanized and automated packaging are packaged in a automatic bread packaging machine with high efficiency and better packaging than manual packaging.
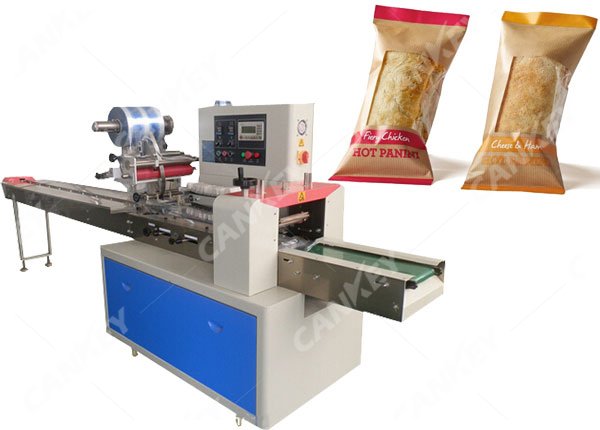

Packaging material requirements:
1. Must meet food hygiene requirements, non-toxic, odorless, tasteless, and will not directly or indirectly contaminate bread.
2. Good airtightness, impervious to water and air, prevent bread from drying and hardening and fragrance loss.
3. For mechanical packaging, the packaging material preferably has a certain mechanical properties to facilitate mechanical handling and protect the bread from mechanical damage.
The packaging materials commonly used in bread are divided into paper and plastic. Paper has oil-resistant paper, wax paper, etc.; plastics include nitrocellulose film, polyethylene, polypropylene, and the like.
First of all, let's first understand the role of bread packaging, in order to ensure that the bread quality meets the hygiene requirements, the bread after cooling or slicing should be packaged immediately.
1. Keep the bread clean and avoid contamination during storage and transportation.
2. Prevent the bread from hardening and extend the shelf life. From the factory to the consumer, the bread needs to be stored and transported for a period of time. As the starch ages and the water evaporates, the bread will harden. After the bread is packaged, it can avoid a lot of moisture loss and keep the bread fresh.
3. Increase the aesthetics of the product. Beautiful packaging can attract consumers' attention, highlight product features, and expand consumption.

Types of bread packaging:
There are many types of bread packaging, which are divided into folding packaging, shrink packaging, and bag packaging according to the packaging form.
According to the packaging method, it can be divided into manual packaging, semi-mechanized packaging and automated packaging. Manual packaging is less restricted by factors such as funds, venues, and product quantities. The application is more flexible, but the disadvantage is that it may not meet the hygiene requirements. Both semi-mechanized and automated packaging are packaged in a automatic bread packaging machine with high efficiency and better packaging than manual packaging.

Packaging material requirements:
1. Must meet food hygiene requirements, non-toxic, odorless, tasteless, and will not directly or indirectly contaminate bread.
2. Good airtightness, impervious to water and air, prevent bread from drying and hardening and fragrance loss.
3. For mechanical packaging, the packaging material preferably has a certain mechanical properties to facilitate mechanical handling and protect the bread from mechanical damage.
The packaging materials commonly used in bread are divided into paper and plastic. Paper has oil-resistant paper, wax paper, etc.; plastics include nitrocellulose film, polyethylene, polypropylene, and the like.

 0086-15515573212
0086-15515573212 info@cankeytech.com
info@cankeytech.com


 Your Location:
Your Location: